学Linux驱动: 应该先了解驱动模型
[导读] Linux设备林林总总,嵌入式开发一个绕不开的话题就是设备驱动开发,在做具体设备驱动开发之前,有必要对Linux设驱动模型有一个相对清晰的认识,将会帮助驱动开发,明白具体驱动接口操作符相应都做些什么。
个人对于驱动模型的理解概括起来就是一句话:利用面向对象编程思想,实现设备分层管理软件体系结构。
注:代码分析基于linux-5.4.31
为啥要驱动模型
随着系统结构演化越来越复杂,Linux内核对设备描述衍生出一般性的抽象描述,形成一个分层体系结构,从而引入了设备驱动模型。这样描述还是不够让人理解,来看一下这些需求就好理解些:
- Linux内核可以在各种体系结构和硬件平台上运行,因此需要最大限度地提高代码在平台之间的可重用性。
- 分层实现也实现了软件工程的高内聚-低耦合的设计思想。低耦合体现在对外提供统一的抽象访问接口,高内聚将相关度紧密的集中抽象实现。
- Linux内核驱动程序模型是先前在内核中使用的所有不同驱动程序模型的统一。 它旨在通过将一组数据和操作整合到全局可访问的数据结构中,来扩展基于基础总线来桥接设备驱动程序。
传统的驱动模型为它们所控制的设备实现了某种类似于树的结构(有时只是一个列表)。不同类型的总线之间没有任何一致性。
驱动模型抽象了啥
当前驱动程序模型为描述总线和总线下可能出现的设备提供了一个通用的、统一的模型。统一总线模型包括一组所有总线都具有的公共属性和一组公共回调,如总线探测期间的设备发现、总线关闭、总线电源管理等。
通用的设备和桥接接口反映了现代计算机的目标:即执行无缝设备“即插即用”,电源管理和热插拔的能力。 特别是,英特尔和微软规定的模型(即ACPI)可确保与x86兼容的系统上几乎任何总线上的几乎所有设备都可以在此范式下工作。 当然,虽然大多数总线都支持其中大多数操作,但并不是每条总线都能够支持所有此类操作。
那么哪些通用需求被抽象出来了呢?
-
电源系统和系统关机,对于电源管理与系统关机对于设备相关的操作进行抽象实现。关机为什么要被抽象出来管理,比如设备操作正在进行此时系统收到关机指令,那么在设备模型层就会遍历系统设备硬件,确保系统正确关机。
-
用户空间访问:sysfs虚拟文件系统实现与设备模型对外的访问抽象,这也是为什么说Linux 设备也是文件的由来。实际从软件架构层面看,这其实是一个软件桥接模块,抽象出统一用户访问接口,桥接了设备驱动。
-
热插拔管理:热插拔管理机制定义统一的抽象接口操作符kset_hotplug_ops,不同设备利用操作符实现差异化。
-
设备类型:设备分类机制,从高层级抽象描述设备类型,具体可以在sysfs下面体现。
用户空间访问
由于具有系统中所有设备的完整分层视图,因此将完整的分层视图导出到用户空间变得相对容易。 这是通过实现名为sysfs虚拟文件系统来完成的。
sysfs的自动挂载通常是通过/etc/fstab文件中的以下条目来完成的:
none /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
对于Debian系统而言,可能在/lib/init/fstab采用下面的形式挂载:
none /sys sysfs nodev,noexec,nosuid 0 0
当然也可以采用手动方式挂载:
# mount -t sysfs sysfs /sys
当将设备插入树中时,都会为其创建一个目录。该目录可以填充在发现的每个层(全局层,总线层或设备层)中。
全局层当前创建两个文件-‘name‘和‘power‘。 前者报告设备名称。 后者报告设备的当前电源状态。 它还将用于设置当前电源状态。
总线层为探测总线时发现的设备创建文件。 例如,PCI层当前为每个PCI设备创建“ irq”和“resource”文件。
特定于设备的驱动程序也可以在其目录中导出文件,以暴露特定于设备的数据或可用接口。
驱动模型实现
先来梳理一下内部几个主要与驱动模型相关的数据结构:
./include/linux/Device.h 定义设备驱动主要数据结构
- bus_type:抽象描述总线类型,如USB/PCI/I2C/MMC等
- device_driver:实现具体连接在总线上的设备驱动。
- device:描述连接在总线上的设备
./include/linux/Kobject.h中定义了隐藏在后台的类似于基类的数据结构:
- kset:可以认为是kobject的顶层容器类。每个kset内部都包含了自己的kobject.
- kobject:在 sysfs 中出现的每个对象都对应一个 kobject, 它和内核交互来创建它的可见表述,每一个 kobject 对应 文件系统 /sys 里的一个 目录,目录的名字就是结构体中的 name

bus_type
bus_type用以驱动总线,具体的驱动USB/I2C/PCI/MMC等:
- 注册总线,利用bus_register注册总线,bus_unregister删除总线。如下例子,每种总线须定义一个bus_type对象,并利用bus_register注册总线,或bus_unregister删除总线。
/*i2c-core-base.c*/
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.match = i2c_device_match,
.probe = i2c_device_probe,
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_bus_type);
static int __init i2c_init(void)
{
int retval;
retval = of_alias_get_highest_id("i2c");
down_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
if (retval >= __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)
__i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num = retval + 1;
up_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
/*注册I2C总线*/
retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type);
if (retval)
return retval;
is_registered = true;
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
i2c_adapter_compat_class = class_compat_register("i2c-adapter");
if (!i2c_adapter_compat_class) {
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto bus_err;
}
#endif
retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver);
if (retval)
goto class_err;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC))
WARN_ON(of_reconfig_notifier_register(&i2c_of_notifier));
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ACPI))
WARN_ON(acpi_reconfig_notifier_register(&i2c_acpi_notifier));
return 0;
class_err:
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class);
bus_err:
#endif
is_registered = false;
/*错误时删除总线*/
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
return retval;
}
- 注册适配器驱动程序(USB控制器,I2C适配器等),以检测连接的设备,并提供与设备的通信机制
- 图中的match函数接口用于将驱动程序与设备进行匹配。match回调的目的是使总线有机会通过比较驱动程序支持的设备ID与特定设备的设备ID来确定特定驱动程序是否支持特定设备,而不会牺牲特定于总线的功能或类型安全性 。当向总线注册驱动程序时,将遍历总线的设备列表,并为每个没有与之关联的驱动程序的设备调用match回调。
- 提供API函数以实现适配器驱动以及设备驱动。
- 同时dev_pm_ops *pm实现对于总线的功耗管理接口抽象。对于特定总线实现这个操作符对应的函数。
struct dev_pm_ops {
int (*prepare)(struct device *dev);
void (*complete)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
int (*freeze)(struct device *dev);
int (*thaw)(struct device *dev);
int (*poweroff)(struct device *dev);
int (*restore)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend_late)(struct device *dev);
int (*resume_early)(struct device *dev);
int (*freeze_late)(struct device *dev);
int (*thaw_early)(struct device *dev);
int (*poweroff_late)(struct device *dev);
int (*restore_early)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend_noirq)(struct device *dev);
int (*resume_noirq)(struct device *dev);
int (*freeze_noirq)(struct device *dev);
int (*thaw_noirq)(struct device *dev);
int (*poweroff_noirq)(struct device *dev);
int (*restore_noirq)(struct device *dev);
int (*runtime_suspend)(struct device *dev);
int (*runtime_resume)(struct device *dev);
int (*runtime_idle)(struct device *dev);
};
- iommu_ops 操作符提供总线相关的IOMMU抽象。
- 设备驱动注册到总线上时,将在sysfs管理总线/设备/设备驱动的层次关系,以PCI为例:
/*在总线上注册的驱动程序会在总线的驱动程序目录中获得一个目录*/
/sys/bus/pci/
|-- devices
`-- drivers
|-- Intel ICH
|-- Intel ICH Joystick
|-- agpgart
`-- e100
/*在该类型的总线上发现的每个设备都会在总线的设备目录中获得到物理层次结构中该设备目录的符号链接*/
/sys/bus/pci/
|-- devices
| |-- 00:00.0 -> ../../../root/pci0/00:00.0
| |-- 00:01.0 -> ../../../root/pci0/00:01.0
| `-- 00:02.0 -> ../../../root/pci0/00:02.0
`-- drivers
- 总线属性:bus_groups/设备属性dev_groups/驱动属性drv_groups。
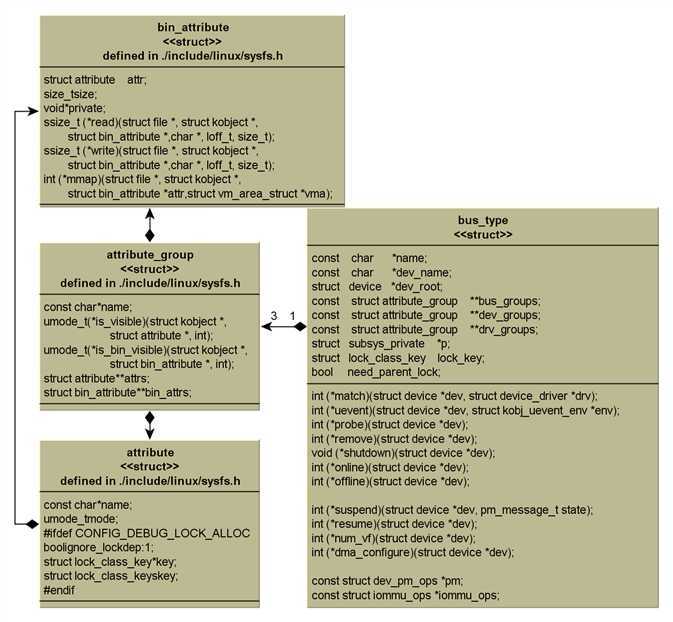
device
-
作用:抽象描述具体的设备
-
设备注册:发现设备的总线驱动程序使用下面的函数来向内核注册设备
int device_register(struct device * dev);
- 利用device_unregister()从总线上删除设备
device_driver
- 作用:抽象描述连接在总线上的具体设备的驱动
- 驱动注册,通过下面的函数将设备驱动程序注册
int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv);
- 使用它使用以下命令从驱动程序目录中添加和删除属性
int driver_create_file(struct device_driver *, const struct driver_attribute *);
void driver_remove_file(struct device_driver *, const struct driver_attribute *);
class
- 作用:抽象设备的高层视图,描述的是设备的集合。抽象了同类型的设备的底层实现细节。比如所有的网络接口都位于/sys/class/net下
- struct subsys_private *p描述类链表
kobject/kset
- kobject类似于面向对象中的内核基类,内核利用它将各个对象连接起来组成分层的机构体系,其parent指针将形成一个树状分层结构。
- kset内部包含了kobject。重心在描述对象的聚集于集合。这也是set一词的含义。每一个kset添加到系统中,都将在sysfs中创建一个目录
- kobject/kset一起实现了sysfs虚拟文件系统中设备/总线/设备驱动树状分层结构的最关键的底层实现由来。
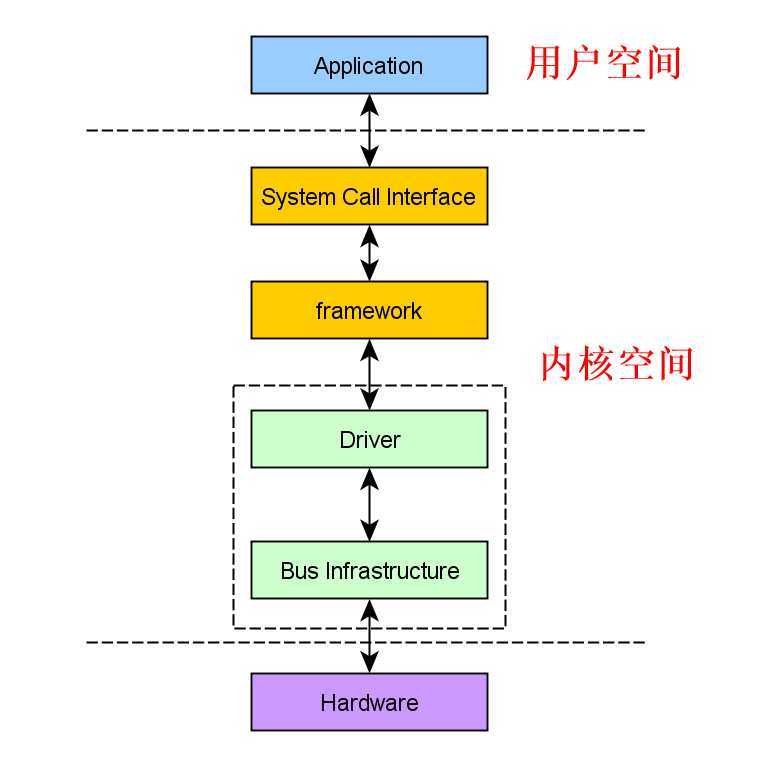
总体上而言:
通过上面一些关键数据结构关系分析,总线设备驱动模型最终目的是实现如下这样一个分层驱动模型。
文章出自微信公众号:嵌入式客栈,更多内容,请关注本人公众号,严禁商业使用,违法必究

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/embInn/p/13034226.html
