java-Map集合
时间:2020-05-31 23:07:01
收藏:0
阅读:63

/* Map集合的特点: Map集合市一个双列集合,一个元素包含两个值:一个key,一个value Map集合中的元素,key和value的数据类型可以相同,也可以不同 Map集合中的元素,key不允许重复的,value是可以重复的 Map集合中的元素,key和value是一一对应的 */
/* HashMap集合特点; 底层是哈希表:查询速度非常块 1.8之前是:数组+单向链表 1.8之后是:数组+单向链表/红黑树(当链表长度超过8):提高查询的速度 hashmap集合是一个无序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序可能不一样 LinkedHashMap集合特点: 底层是哈希表+链表(保证迭代的顺序) 是一个有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的 */
Map接口常用的方法:

/* V put(K key, V value) 将指定的值与该映射中的指定键相关联(可选操作)。 返回值是 V 存储键值对的时候,key如果不重复,返回v是null 如果重复,会使用新的value替换map中重复的value,并返回被替换的value值 */ public static void show1(){ Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); String v1 = map.put("AAAA","1111"); System.out.println(v1); String v2 = map.put("AAAA","aaaa"); System.out.println(v2);//返回被替换的值 map.put("BBBB","2222"); map.put("CCCC","3333"); map.put("DDDD","3333"); System.out.println(map); }
/* V remove(Object key) 如果存在(从可选的操作),从该地图中删除一个键的映射。 返回值:V Key存在,返回被删除的值 key不存在,返回null */ public static void show2(){ Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("AAA",11); map.put("BBB",33); map.put("CCC",22); map.put("DDD",41); System.out.println(map);//{AAA=11, CCC=22, BBB=33, DDD=41} //删除存在的key值 Integer v = map.remove("DDD"); System.out.println(v);//42 System.out.println(map);//{AAA=11, CCC=22, BBB=33} //删除不存在的key值 Integer v2 = map.remove("EEE"); System.out.println(v2);//null }
public static void show3(){ /* V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,再map集合中获取对应的值 返回值: key存在,返回对应的value值 不存在,返回null */ Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("AAA",11); map.put("BBB",33); map.put("CCC",22); map.put("DDD",41); Integer v1 = map.get("CCC"); System.out.println(v1);//22 Integer v2 = map.get("OOO"); System.out.println(v2);//null }
public static void show4(){ /* boolean containsKey 判断集合是否包含指定的键 包含返回true,不包含返回false */ Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("AAA",11); map.put("BBB",33); map.put("CCC",22); map.put("DDD",41); boolean b1 = map.containsKey("AAA"); System.out.println(b1); //true boolean b2 = map.containsKey("OOOO"); System.out.println(b2);//false }
遍历map集合
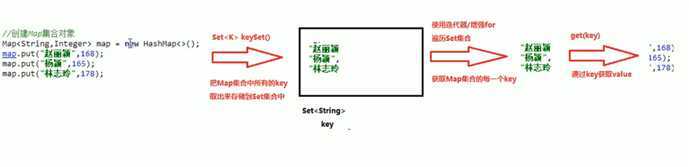
/* map集合的第一中遍历方式,通过键找值得方式 map集合中得方法: Set<K> keySet() 返回此映射中包含得键得Set视图 实现步骤: 使用Map集合中得方法keySet(),把Map集合所有得key取出,存储到一个Set集合里面 通过遍历Set集合,获取Map集合中得每一个key 通过Map集合中得方法get(key),通过key找到value */
public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("AAA",11); map.put("BBB",33); map.put("CCC",22); map.put("DDD",41); Set<String> set = map.keySet(); Iterator<String> it =set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ String key = it.next(); Integer value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key + "=" + value); } System.out.println("###################"); // for (String key:map.keySet())更简洁得做法 for (String key:set){ System.out.println(key + "=" + map.get(key)); } } } /* AAA=11 CCC=22 BBB=33 DDD=41 ################### AAA=11 CCC=22 BBB=33 DDD=41 */
Entry对象
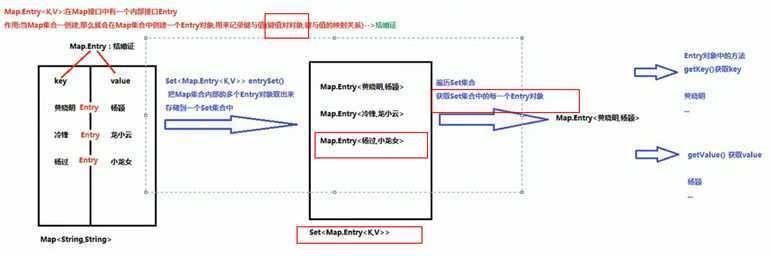
/* 使用 Entry对象遍历 Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 返回此地图中包含的映射的Set视图。 实验不走: 使用Map集合中得方法,entrySet(),把Map集合中多个Entry对象取出来,存储到Set集合 遍历Set集合,获取每一个Entry对象 使用Entry对象里的getKey getValue获取键值对 */
public class Demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("AAA",11); map.put("BBB",33); map.put("CCC",22); map.put("DDD",41); Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> set = map.entrySet(); Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry = it.next(); String key = entry.getKey(); Integer value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + "=" + value); } } } /* AAA=11 CCC=22 BBB=33 DDD=41 */
HashMap存储自定义类型
/* Map集合保证key是唯一的: 作为key的元素,必须重写hashCode和quals方法,以保证key唯一 */
public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { show2(); } //必须重写函数 private static void show2(){ HashMap<Person,String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put(new Person("AAA",11),"aaa"); map.put(new Person("BBB",13),"bbb"); map.put(new Person("AAA",11),"ddd"); map.put(new Person("CCC",21),"ccc"); System.out.println(map); // {Person{name=‘BBB‘, age=13}=bbb, Person{name=‘AAA‘, age=11}=ddd, Person{name=‘CCC‘,
age=21}=ccc} } private static void show1(){ HashMap<String,Person> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("背景",new Person("AAA",11)); map.put("关东",new Person("BBB",31)); map.put("上海",new Person("CVC",21)); map.put("背景",new Person("CC",21)); // 遍历结合 Set<String> set = map.keySet(); for (String s :set){ Person p = map.get(s); System.out.println(s + "=" + p); } } }
LinkedHashMap集合
/* map接口的哈希表和连接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序 底层原理: 哈希表+链表(记录元素的顺序) */
public class Demo8 { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedHashMap<String,String> map2 = new LinkedHashMap<>(); map2.put("AA","aa"); map2.put("cc","cc"); map2.put("BB","bb"); map2.put("AA","dd"); System.out.println(map2); } }
Hashtable集合
/* java.util.Hashtable<k,v> 集合 implaments Map<k,v>接口 Hashtable 底层也是一个哈希表,是一个线程安全的集合,是单线程集合,速度慢 HashMap 底层也是一个哈希表,是一个线程不安全的集合,是多线程的结合,速度块 HashMap集合(之前的集合都可以) 可以存储null键值,和null值 Hashtable 不能存储null值,null键 Hashtable 的子类properties很活跃 properties 是唯一一个和I/O流有关的集合 */
public class Demo11 { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("AA",null); map.put(null,"QQ"); map.put(null,null); System.out.println(map);//{AA=null, null=null} Hashtable<String,String> table = new Hashtable<>(); table.put(null,"DD");//java.lang.NullPointerException table.put("EE","ee"); System.out.println(table); } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/java-quan/p/13021976.html
评论(0)
