Python实现DFA算法,完成实体词匹配和敏感词过滤等功能
时间:2020-04-17 10:49:38
收藏:0
阅读:279
一、什么是DFA算法
DFA 全称为:Deterministic Finite Automaton,即确定有穷自动机。其特征为:有一个有限状态集合和一些从一个状态通向另一个状态的边,每条边上标记有一个符号,其中一个状态是初态,某些状态是终态。但不同于不确定的有限自动机,DFA 中不会有从同一状态出发的两条边标志有相同的符号。
其实对于DFA算法的定义还是有点抽象,下面的图文并茂或许会对你有帮助!
词库的构造
以王八蛋和王八羔子两个敏感词来进行描述,首先构建敏感词库,该词库名称为SensitiveMap,这两个词的二叉树构造为:
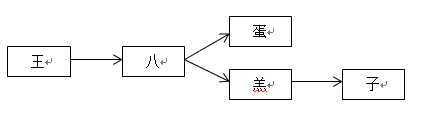
用 hash 表构造为:
1 { 2 "王": { 3 "is_end": false, 4 "八": { 5 "is_end": false, 6 "蛋": { 7 "is_end": true 8 }, 9 "羔": { 10 "is_end": false, 11 "子": { 12 "is_end": true 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 }
此段借鉴于博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/jmcui/p/11925777.html
虽然这篇博客的实现方式是Java,但是对于DFA算法的理解,我觉得是非常透彻的。
二、Python代码实现

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 # @Time:2020/4/15 11:40 4 # @Software:PyCharm 5 __author__ = "JentZhang" 6 import json 7 8 MinMatchType = 1 # 最小匹配规则,如:敏感词库["中国", "中国人"],语句:"我是中国人",匹配结果:我是[中国]人 9 MaxMatchType = 2 # 最大匹配规则,如:敏感词库["中国", "中国人"],语句:"我是中国人",匹配结果:我是[中国人] 10 11 12 class DFAUtils(object): 13 """ 14 DFA算法 15 """ 16 17 def __init__(self, word_warehouse): 18 """ 19 算法初始化 20 :param word_warehouse:词库 21 """ 22 # 词库 23 self.root = dict() 24 # 无意义词库,在检测中需要跳过的(这种无意义的词最后有个专门的地方维护,保存到数据库或者其他存储介质中) 25 self.skip_root = [‘ ‘, ‘&‘, ‘!‘, ‘!‘, ‘@‘, ‘#‘, ‘$‘, ‘¥‘, ‘*‘, ‘^‘, ‘%‘, ‘?‘, ‘?‘, ‘<‘, ‘>‘, "《", ‘》‘] 26 # 初始化词库 27 for word in word_warehouse: 28 self.add_word(word) 29 30 def add_word(self, word): 31 """ 32 添加词库 33 :param word: 34 :return: 35 """ 36 now_node = self.root 37 word_count = len(word) 38 for i in range(word_count): 39 char_str = word[i] 40 if char_str in now_node.keys(): 41 # 如果存在该key,直接赋值,用于下一个循环获取 42 now_node = now_node.get(word[i]) 43 now_node[‘is_end‘] = False 44 else: 45 # 不存在则构建一个dict 46 new_node = dict() 47 48 if i == word_count - 1: # 最后一个 49 new_node[‘is_end‘] = True 50 else: # 不是最后一个 51 new_node[‘is_end‘] = False 52 53 now_node[char_str] = new_node 54 now_node = new_node 55 56 def check_match_word(self, txt, begin_index, match_type=MinMatchType): 57 """ 58 检查文字中是否包含匹配的字符 59 :param txt:待检测的文本 60 :param begin_index: 调用getSensitiveWord时输入的参数,获取词语的上边界index 61 :param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则 62 :return:如果存在,则返回匹配字符的长度,不存在返回0 63 """ 64 flag = False 65 match_flag_length = 0 # 匹配字符的长度 66 now_map = self.root 67 tmp_flag = 0 # 包括特殊字符的敏感词的长度 68 69 for i in range(begin_index, len(txt)): 70 word = txt[i] 71 72 # 检测是否是特殊字符,eg"法&&轮&功..." 73 if word in self.skip_root and len(now_map) < 100: 74 # len(nowMap)<100 保证已经找到这个词的开头之后出现的特殊字符 75 # eg"情节中,法&&轮&功..."这个逗号不会被检测 76 tmp_flag += 1 77 continue 78 79 # 获取指定key 80 now_map = now_map.get(word) 81 if now_map: # 存在,则判断是否为最后一个 82 # 找到相应key,匹配标识+1 83 match_flag_length += 1 84 tmp_flag += 1 85 # 如果为最后一个匹配规则,结束循环,返回匹配标识数 86 if now_map.get("is_end"): 87 # 结束标志位为true 88 flag = True 89 # 最小规则,直接返回,最大规则还需继续查找 90 if match_type == MinMatchType: 91 break 92 else: # 不存在,直接返回 93 break 94 95 if tmp_flag < 2 or not flag: # 长度必须大于等于1,为词 96 tmp_flag = 0 97 return tmp_flag 98 99 def get_match_word(self, txt, match_type=MinMatchType): 100 """ 101 获取匹配到的词语 102 :param txt:待检测的文本 103 :param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则 104 :return:文字中的相匹配词 105 """ 106 matched_word_list = list() 107 for i in range(len(txt)): # 0---11 108 length = self.check_match_word(txt, i, match_type) 109 if length > 0: 110 word = txt[i:i + length] 111 matched_word_list.append(word) 112 # i = i + length - 1 113 return matched_word_list 114 115 def is_contain(self, txt, match_type=MinMatchType): 116 """ 117 判断文字是否包含敏感字符 118 :param txt:待检测的文本 119 :param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则 120 :return:若包含返回true,否则返回false 121 """ 122 flag = False 123 for i in range(len(txt)): 124 match_flag = self.check_match_word(txt, i, match_type) 125 if match_flag > 0: 126 flag = True 127 return flag 128 129 def replace_match_word(self, txt, replace_char=‘*‘, match_type=MinMatchType): 130 """ 131 替换匹配字符 132 :param txt:待检测的文本 133 :param replace_char:用于替换的字符,匹配的敏感词以字符逐个替换,如"你是大王八",敏感词"王八",替换字符*,替换结果"你是大**" 134 :param match_type:匹配规则 1:最小匹配规则,2:最大匹配规则 135 :return:替换敏感字字符后的文本 136 """ 137 tuple_set = self.get_match_word(txt, match_type) 138 word_set = [i for i in tuple_set] 139 result_txt = "" 140 if len(word_set) > 0: # 如果检测出了敏感词,则返回替换后的文本 141 for word in word_set: 142 replace_string = len(word) * replace_char 143 txt = txt.replace(word, replace_string) 144 result_txt = txt 145 else: # 没有检测出敏感词,则返回原文本 146 result_txt = txt 147 return result_txt 148 149 150 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 151 dfa = DFAUtils(word_warehouse=["王八蛋", "王八羔子", ‘你妈的‘, ‘你奶奶的‘, ‘你妈的啊‘]) 152 print(‘词库结构:‘, json.dumps(dfa.root, ensure_ascii=False)) 153 # 待检测的文本 154 msg = ‘你是王$八!蛋,你&&奶 奶的‘ 155 print(‘是否包含:‘, dfa.is_contain(msg)) 156 print(‘相匹配的词:‘, dfa.get_match_word(msg)) 157 print(‘替换包含的词:‘, dfa.replace_match_word(msg))
执行结果:

1 C:\Users\admin\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python37\python3.exe D:/Projects/JDMFAnalysisSystem/utils/dfa_utils.py 2 词库结构: {"王": {"is_end": false, "八": {"is_end": false, "蛋": {"is_end": true}, "羔": {"is_end": false, "子": {"is_end": true}}}}, "你": {"is_end": false, "妈": {"is_end": false, "的": {"is_end": false, "啊": {"is_end": true}}}, "奶": {"is_end": false, "奶": {"is_end": false, "的": {"is_end": true}}}}} 3 是否包含: True 4 相匹配的词: [‘王$八!蛋‘, ‘你&&奶 奶的‘] 5 替换包含的词: 你是*****,******* 6 7 Process finished with exit code 0
提示:
代码可以直接复制到本地执行,执行没问题,然后再慢慢消化整个实现的思路哦。
关于DFA算法的Python实现,我是借鉴于:https://github.com/morenjiujiu/sensitive_content_filter
二、总结
本文也只是通过python简易实现了dfa的一些基本算法。对于一些词的过滤,还要考虑到无意义字符的干扰。比如:
对于“王*八&&蛋”这样的词,中间填充了无意义的字符来混淆,在我们做敏感词搜索时,同样应该做一个无意义词的过滤,当循环到这类无意义的字符时进行跳过,避免干扰。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/JentZhang/p/12718092.html
评论(0)

