IO 流
------------恢复内容开始------------
一、流的简介
输入流:把硬盘中的数据读取到内存中
输出流:把内存中的数据读取到硬盘中
1字符=2字节 1字节=8位
1.2顶级父类

二、字节流
2.1、一切皆为字节
一切文本数据(视频、图片、文本)在存储时,都是以二进制数字的形式进行保存,都是一个个的字节,那么传输时一样如此。所以字节流可以传输任意的数据。在操作流的时候,我们要时刻明确,无论使用什么样的流对象,底层传输始终为二进制数据。
2.2字节输出流
(1)成员方法
void |
close() 关闭此输出流并释放与此流关联的任何系统资源。 |
void |
flush() 刷新输出流,使缓存数据被写出来。 |
void |
write(byte[] b) 写 b.length字节从指定的字节数组的输出流。 |
void |
write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 写 len字节指定字节数组中的偏移 off开始到输出流。 |
abstract void |
write(int b) 将指定的字节写入该输出流中。 |
(2)构造方法
1、FileOutputStream(String name) 创建一个向具有指定名称的文件中写入数据的文件输出流。
String name:目的地是一个文件路径
2、FileOutputStream(File file) 创建一个向指定File对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流。
File file:目的地是一个文件
构造方法的作用:
1、创建一个FileOutputStream对象
2、会根据构造方法中传递的文件/文件路径,创建一个空的文件
3、会把FileOutputStream对象指向创建好的文件
3、写入数据的原理(内存-->硬盘)
java程序-->JVM-->OS(操作系统)-->OS调用写数据的方法-->把数据写入到文件中
package IO; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递写入数据的目的地 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\a.txt");//会抛出文件找不到异常,用try-catch fos.write(97);//写进去的是二进制数据所对应的字符a fos.close(); } }
存入结果:

package IO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递写入数据的目的地 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt"));//会抛出文件找不到异常,同try-catch //在文件中显示100,写个字节 fos.write(49); fos.write(48); fos.write(48); //释放资源 fos.close(); } }
存入结果:

每次都用writer()写入一个字符,会显得特别麻烦,public void write(byte[] b):将b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流
一次写多个字节:
如果写的第一个字节是正数(0--127),那么显示的时候会查询ASCII表
如果写的第一个字节是负数(0--127),那么第一个字节会和第二个字节组成一个中文显示,查询系统默认码表(GBK)
package IO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递写入数据的目的地 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt"));//会抛出文件找不到异常,同try-catch byte[] bytes1 = {65,66,67,68,69};//ABCDEFG byte[] bytes2 = {-65,-66,-67,68,69};//ABCDEFG fos.write(bytes1); fos.write(bytes2); //释放资源 fos.close(); } }
写入结果:

public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 把字节数组的一部分写入到文件中。
package IO; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递写入数据的目的地 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt"));//会抛出文件找不到异常,同try-catch byte[] bytes1 = {65,66,67,68,69};//ABCDEFG fos.write(bytes1,1,2); //释放资源 fos.close(); } }

4、读出数据的原理(硬盘-->内存)
Inputstream-字节输入流
读取过程:
4.1、一次读取单个字符:

public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt"));//会抛出文件找不到异常,同try-catch int len = fos.read(); System.out.println(len); len = fos.read(); System.out.println(len); len = fos.read(); System.out.println(len); len = fos.read(); System.out.println(len); fos.close(); } }
输出结果:
104 101 108 108
4.2、一次读取多个字符:

public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递写入数据的目的地 FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt"));//会抛出文件找不到异常,同try-catch // byte[] byte2 = "hello java!".getBytes(); byte[] bytes = new byte[2]; int len = fos.read(bytes);//读取到并放入bytes数组中 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)); System.out.println(new String(bytes)); //释放资源 fos.close(); } }
输出结果:
[104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 106, 97, 118, 97, 33, 0] hello java!
4.2、一次写入多个字符:
package IO; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建一个FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递写入数据的目的地 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt"));//会抛出文件找不到异常,同try-catch byte[] bytes1 = {65,66,67,68,69};//ABCDEFG byte[] bytes2 = {-65,-66,-67,68,69};//ABCDEFG fos.write(bytes1); fos.write(bytes2); //释放资源 fos.close(); } }
五、关于try{}--catch{}--finally{}和流的关系
异常捕获try--catch--finally格式:
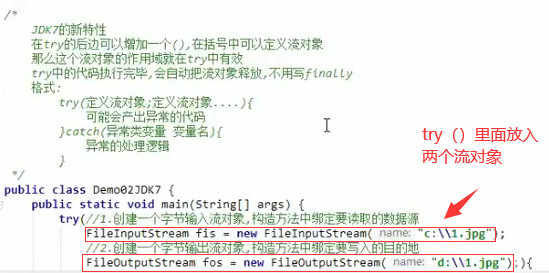
例子:利用try--catch捕获异常形式,把a.txt中的数据写入b.txt中
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //把文件a.txt中的数据写入b.txt中,实例化两个文件输入输出流 FileReader a = new FileReader("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\a.txt"); FileWriter b = new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt",true);//会抛出文件找不到异常,同try-catchFileInputStream b = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\b.txt")); try(a;b)//try()放入流对象 { int len=0; while ((len = a.read())!=-1) { b.write(len); } }catch(IOException e) { System.out.println(e); } a.close(); b.close(); }
6、Properties集合与流的使用
properties集合:是一个和流结合使用的键值映射集合,properties集合的键-值都默认为字符串,常用的方法有store、load。
store:负责把propertis映射集合中的数据存储到硬盘中;
load:负责把硬盘中的数据加载到properties映射集合中;
(1)通过store方法,把properties映射集合把数据写入指定文件中
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty("哈哈","java"); properties.setProperty("你好","c语言"); properties.setProperty("哈喽","PHP"); //负责把数据从集合中加载至硬盘中的文件 FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\a.txt"); properties.store(fileWriter,"save date"); } }
运行结果:
(2)通过load方法,把数据从文件读取到缓冲区中
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Properties properties = new Properties(); //实例化一个文件字符流,并通过properties.load方法将文件内容加载至properties映射缓冲剂区; properties.load(new FileReader("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\a.txt")); //在这个属性列表中返回一组键,其中键和它的对应值是字符串,包括在默认属性列表中的不同键,如果同一个名称的一个键没有从主要属性列表中找到。 Set<String> set = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for(String s: set ) { String value = properties.getProperty(s); System.out.println("key="+s+" "+"value="+value); } } }
7、缓冲流:bufferedStream
(1)作用:(1)不用缓冲区,快递小哥取快递,为了熟悉环境,一次送一个快递
(2)用缓冲区,快递小哥取快递,一次送五个快递,节省时间与效率
(2)分类:bufferedInputStream--字节缓冲输入流、bufferedOutputStrea--字节缓冲输出流
bufferedWriter--字符缓冲输入流、bufferedReader--字符缓冲输出流
(3)通过字节缓冲输出流BufferOutputStream,向缓冲区以字节的形式向文件写入数据:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建一个FileOutputstream对象 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\a.txt"); //2.创建BufferOutputStream对象,对象的构造方法中传递FileoutputStream对象,提高对象的利用率 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.使用BufferedOutputStream 的write方法将数据写入缓冲区中; bos.write("我把数据写入到缓冲区中".getBytes()); //4.使用BufferOutputSteam 对象中的flush方法将缓冲区的数据刷新到文件中; bos.flush(); } }
(4)通过字节缓冲输入流BufferInputStream,向缓冲区以字节的形式向文件读取数据:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建一个FileInputstream对象 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\a.txt"); //2.创建BufferInputStream对象,对象的构造方法中传递FileInputStream对象,提高对象的利用率 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); byte[] bytes = new byte[50]; //3.使用BufferedInputStream 的read方法将数据写入缓冲区中; int len=0; while ((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1); { System.out.print(new String(bytes)); } //4.使用BufferInputSteam 对象中的flush方法将缓冲区的数据刷新到文件中; }
(5)使用buffered缓冲流和不适用缓冲流的读取速度时间比较:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Long s = System.currentTimeMillis(); BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\ibear\\Documents\\WeChat Files\\xwnaxcm\\a.txt")); byte[] bytes = new byte[50]; int len = 0; while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) ; { System.out.println(new String(bytes)); } Long e = System.currentTimeMillis(); Long c = e - s; System.out.print("本次使用缓冲流读取时间:" + c + "毫秒"); } }
运行结果:
我把数据写入到缓冲区中
本次使用缓冲流读取时间:8毫秒
------------恢复内容结束------------
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ibear/p/12545865.html
